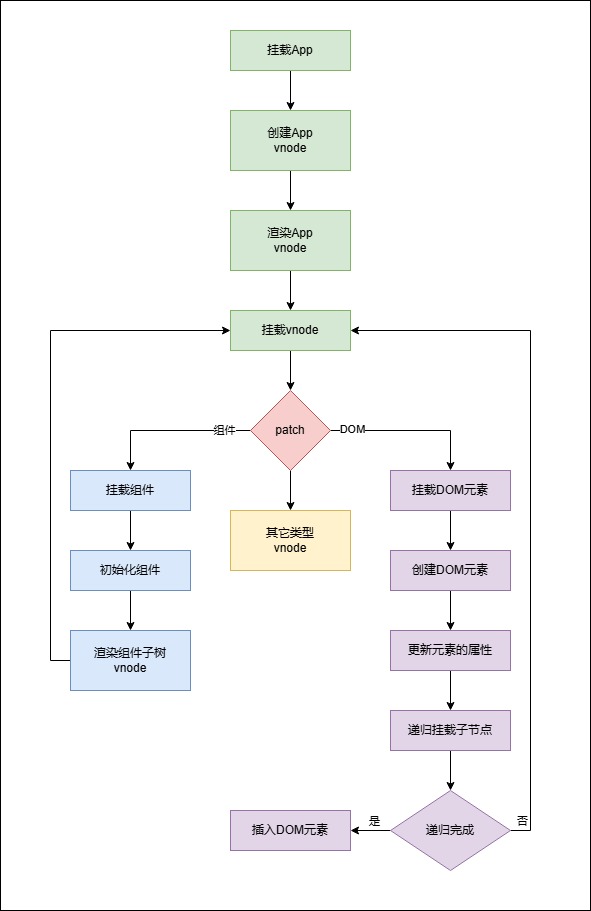
[vue3] vue3初始化渲染流程
组件初次渲染流程
组件是对DOM树的抽象,组件的外观由template定义,模板在编译阶段会被转化为一个渲染函数,用于在运行时生成vnode。即组件在运行时的渲染步骤是:
vnode是一个用于描述视图的结构和属性的JavaScript对象。vnode是对真实DOM的一层抽象。
使用
vnode的优点:
- 相比于直接操作
DOM,在需要频繁更新视图的场景下,可以将多次操作应用在vnode上,再一次性地生成真实DOM,可以避免频繁重排重绘导致的性能问题;vnode是抽象的视图层,具有平台无关性,上层代码可移植性强。
应用程序初始化
对于一个vue-app来说,整个组件树由根组件开始渲染。为了找到根组件的渲染入口,从应用程序的初始化过程开始分析。
在Vue2中,初始化应用的代码:
import Vue from 'vue';
import App from './App';
const app = new Vue({
render: h=>h(App)
});
app.$mount('#app');
在Vue3中,初始化应用的代码:
import { createApp } from 'vue';
import App from './App';
const app = createApp(App);
app.mount('#app');
对比二者的代码可以看出,本质都是把App组件挂载到了#appDOM节点上。
本文主要关注
Vue3。
Vue3的createApp的实现大致如下:
首先,createApp函数由createAppAPI根据对应的render对象构建得到。
export function createAppAPI<HostElement>(
render: RootRenderFunction<HostElement>,
hydrate?: RootHydrateFunction,
): CreateAppFunction<HostElement> {
return function createApp(rootComponent, rootProps = null) {
//...
}
}
源码位置:core/packages/runtime-core/src/apiCreateApp.ts at main · vuejs/core (github.com)
render对象由baseCreateRenderer函数创建,根据不同的环境创建不同的render对象(常见的是浏览器环境下用来渲染DOM)。
并由render对象来决定createApp函数的实现:
// baseCreateRenderer函数的返回值
return {
render,
hydrate,
createApp: createAppAPI(render, hydrate),
}
这种根据不同环境构建不同render对象的操作是为了实现跨平台。
接下来回到createApp内部。
createApp应用工厂模式,在内部创建app对象,实现了mount方法,mount方法就是用来挂载组件的。
function createApp(rootComponent, rootProps = null){
// ...
const app: App = {
// ...
mount(
rootContainer: HostElement,
isHydrate?: boolean,
namespace?: boolean | ElementNamespace,
): any{
// mount的具体实现,这里省略了很多代码...
// 1. 创建vnode
const vnode = createVNode(rootComponent, rootProps)
// 2. 渲染vnode
render(vnode, rootContainer, namespace)
}
// ...
}
return app;
}
在整个app对象创建过程中,Vue3通过闭包和函数柯里化等技巧实现了参数保留。
例如上面的mount方法内部实际上会使用render函数将vnode挂载到container上。而render由createAppAPI调用时传入。这就是闭包的应用。
上面提到的app对象中对mount的实现位于packages/runtime-core,也就是说是与平台无关的,内部都是对抽象的vnode、rootContainer进行操作,不一定是DOM节点。
Vue3将浏览器相关的DOM的实现移到了packages/runtime-dom中,在index.ts中可以看到ensureRenderer函数就调用了runtime-core中上述提到的createRenderer方法,传入了DOM相关的配置,用于获取一个专门用于浏览器环境的renderer。
源码位置:core/packages/runtime-dom/src/index.ts at main · vuejs/core (github.com)
在runtime-dom的index.ts中,我们从createApp函数入手,观察到它调用了ensureRenderer来获取一个适配浏览器环境的renderer,并调用其对应的createApp函数。
export const createApp = ((...args) => {
const app = ensureRenderer().createApp(...args)
// ......
const { mount } = app
// 重写mount方法
app.mount = (containerOrSelector: Element | ShadowRoot | string): any => {
// 标准化容器:将字符串选择器转换为DOM对象
const container = normalizeContainer(containerOrSelector)
if (!container) return
const component = app._component
// 如果组件对象没有定义render函数和template模板,则取容器的innerHTML作为模板内容
if (!isFunction(component) && !component.render && !component.template) {
// 使用innerHTML需要注意安全性问题
component.template = container.innerHTML
// ......
}
// 挂载前删除容器的内容
container.innerHTML = ''
// 走runtime-core中实现的标准流程进行挂载
const proxy = mount(container, false, resolveRootNamespace(container))
// ......
return proxy
}
return app
}) as CreateAppFunction<Element>
阶段性总结:
-
重写
mount的原因:runtime-core中的mount:实现标准化挂载流程;runtime-dom中的mount:实现DOM节点相关的预处理,然后调用runtime-core中的mount进行挂载;
-
runtime-dom中mount的流程:-
标准化容器:如果传入字符串选择器,那么调用
document.querySelector将其转换为DOM对象; -
检查组件是否存在
render函数和template对象,如果没有则使用容器的innerHTML作为模板;使用
innerHTML需要注意安全性问题。 -
删除容器原先的
innerHTML内容; -
调用
runtime-core中实现的mount方法走标准化流程挂载组件到DOM节点上。
-
从app.mount方法调用后,才真正开始组件的渲染流程。
接下来,回到runtime-core中关注渲染流程。
核心渲染流程
这一流程中主要做了两件事:创建vnode和渲染vnode。
vnode是用来描述DOM的JavaScript对象,在Vue中既可以描述普通DOM节点,也可以描述组件节点,除此之外还有纯文本vnode和注释vnode。
可以在runtime-core的vnode.ts文件中找到vnode的类型定义:core/packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts at main · vuejs/core (github.com)
内容较多,这里不做展示,比较核心的属性有比如:
type:组件的标签类型;props:附加信息;children:子节点,vnode数组;
除此之外,Vue3还为vnode打上了各种flag来做标记,在patch阶段根据不同的类型执行相应的处理逻辑。
创建vnode
在mount方法的实现中,通过调用createVNode函数创建根组件的vnode:
const vnode = createVNode(rootComponent, rootProps);
在vnode.ts中可以找到createVNode函数的实现:core/packages/runtime-core/src/vnode.ts at main · vuejs/core (github.com)
大致思路如下:
function _createVNode(
type: VNodeTypes | ClassComponent | typeof NULL_DYNAMIC_COMPONENT,
props: (Data & VNodeProps) | null = null,
children: unknown = null,
patchFlag: number = 0,
dynamicProps: string[] | null = null,
isBlockNode = false,
): VNode{
// ...
// 标准化class和style这些样式属性
if(props){
// ...
}
// 对vnode类型信息编码(二进制)
const shapeFlag = isString(type)
? ShapeFlags.ELEMENT
: __FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && isSuspense(type)
? ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE
: isTeleport(type)
? ShapeFlags.TELEPORT
: isObject(type)
? ShapeFlags.STATEFUL_COMPONENT
: isFunction(type)
? ShapeFlags.FUNCTIONAL_COMPONENT
: 0
// 调用工厂函数构建vnode对象
return createBaseVNode(
type,
props,
children,
patchFlag,
dynamicProps,
shapeFlag,
isBlockNode,
true,
)
}
接下来看一下createBaseVNode的大致实现(这个函数也位于vnode.ts文件内):
function createBaseVNode(
// vnode部分属性的值
){
const vnode = {
type,
props,
// ...很多属性
} as VNode
// 标准化children:讨论数组或者文本类型
if (needFullChildrenNormalization) {
normalizeChildren(vnode, children)
}
return vnode
}
渲染vnode
创建好vnode之后就是渲染的过程,在mount中使用render函数渲染创建好的vnode。
render的标准化流程的实现位于runtime-core的renderer.ts中:
源码位置:core/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts at main · vuejs/core (github.com)
const render: RootRenderFunction = (vnode, container, namespace) => {
if (vnode == null) {
// 销毁组件
if (container._vnode) {
unmount(container._vnode, null, null, true)
}
} else {
// 创建或者更新组件
patch(
container._vnode || null,
vnode,
container,
null,
null,
null,
namespace,
)
}
if (!isFlushing) {
isFlushing = true
flushPreFlushCbs()
flushPostFlushCbs()
isFlushing = false
}
// 缓存vnode节点,表示已经渲染
container._vnode = vnode
}
- 如果
vnode不存在,则调用unmount销毁组件; - 如果
vnode存在,那么调用patch创建或者更新组件; - 将
vnode缓存到容器对象上,表示已渲染。
patch函数的前两个参数分别是旧vnode和新vnode。
- 初次调用,则
container._vnode属性返回undefined,短路运算符传入null,则patch内部走创建逻辑;调用过后会将创建的vnode缓存到container._vnode; - 后续调用的
container._vnode表示上一次创建的vnode,不为null,传入patch后走更新逻辑。
patch的实现
patch本意是打补丁,这个函数有两个功能:
- 根据
vnode挂载DOM; - 比较新旧
vnode更新DOM。
这里只讨论初始化流程,故只记录如何挂载
DOM,更新流程这里不做介绍。
源码位置:core/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts at main · vuejs/core (github.com)
const patch: PatchFn = (
n1,
n2,
container,
anchor = null,
parentComponent = null,
parentSuspense = null,
namespace = undefined,
slotScopeIds = null,
optimized = __DEV__ && isHmrUpdating ? false : !!n2.dynamicChildren,
) => {
// 二者相同,不需要更新
if (n1 === n2) {
return
}
// vnode类型不同,直接卸载旧节点
if (n1 && !isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
anchor = getNextHostNode(n1)
unmount(n1, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
n1 = null
}
// ......
const { type, ref, shapeFlag } = n2
switch (type) {
case Text:
// 处理文字节点
break
case Comment:
// 处理注释节点
break
case Static:
// 静态节点
break
case Fragment:
// Fragment节点
break
default:
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ELEMENT) {
// 处理普通DOM元素
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.COMPONENT) {
// 处理组件
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TELEPORT) {
// 处理teleport
} else if (__FEATURE_SUSPENSE__ && shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.SUSPENSE) {
// 处理suspense
} else if (__DEV__) {
// 报错:vnode类型不在可识别范围内
warn('Invalid VNode type:', type, `(${typeof type})`)
}
}
}
这里只关注前三个函数参数:
n1:旧vnode,为null则表示初次挂载;n2:新vnode;container:挂载的目标容器。
patch在其内部调用了processXXX处理不同类型的vnode,这里只关注组件类型和普通DOM节点类型。
对组件的处理
处理组件调用的是processComponent函数:
processComponent
const processComponent = (
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
// ... 其它参数
) => {
if (n1 == null) {
// 挂载组件
mountComponent(n2, container, /*...other args*/)
} else {
// 更新组件
updateComponent(n1, n2, optimized)
}
}
// 这里还有很多其它参数省略了,函数体内还处理了`keep-alive`的情况,具体可以自己看源码。
- 挂载组件使用
mountComponent函数; - 更新组件使用
updateComponent函数。
mountComponent
源码位置:core/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts at main · vuejs/core (github.com)
这个函数处理了较多边界情况,这里只展示主要的步骤:
const mountComponent: MountComponentFn = (
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
namespace: ElementNamespace,
optimized,
) => {
// 创建组件实例
const instance: ComponentInternalInstance =
(initialVNode.component = createComponentInstance(
initialVNode,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
))
// 设置组件实例
setupComponent(instance, false, optimized)
// 设置并运行带副作用的渲染函数
setupRenderEffect(
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
namespace,
optimized,
)
}
- 创建组件实例:工厂模式创建组件实例对象;
- 设置组件实例:
instance记录了许多组件相关的数据,setupComponent这一步主要是对props、slots等属性进行初始化。
接下来重点看一下setupRenderEffect函数的实现。
setupRenderEffect
setupRenderEffect 函数的主要工作是设置一个响应式效果 (ReactiveEffect),并创建一个调度任务 (SchedulerJob) 来管理组件的渲染和更新。首次渲染和后续更新的逻辑都封装在 componentUpdateFn 中。
简化后的代码:
const setupRenderEffect: SetupRenderEffectFn = (
instance,
initialVNode,
container,
anchor,
parentSuspense,
namespace: ElementNamespace,
optimized,
) => {
// 组件更新函数
const componentUpdateFn = () => {
if (!instance.isMounted) {
// 首次挂载逻辑
instance.subTree = renderComponentRoot(instance)
patch(null, instance.subTree, container, anchor, instance, parentSuspense, namespace)
instance.isMounted = true
} else {
// 后续更新逻辑
const nextTree = renderComponentRoot(instance)
patch(instance.subTree, nextTree, container, anchor, instance, parentSuspense, namespace)
instance.subTree = nextTree
}
}
// 创建响应式效果
const effect = (instance.effect = new ReactiveEffect(componentUpdateFn, NOOP))
// 创建调度任务
const update: SchedulerJob = (instance.update = () => {
if (effect.dirty) {
effect.run()
}
})
// 立即执行更新函数
update()
}
setupRenderEffect内部主要包含了3个函数:
componentUpdateFn的主要作用是在组件首次挂载和后续更新时执行相应的渲染逻辑,确保组件的虚拟 DOM 树与实际的 DOM 树保持同步,并执行相关的生命周期钩子函数。effect封装了组件的渲染逻辑,负责在响应式依赖变化时触发重新渲染。update是调度任务,负责在适当的时机检查和触发effect,确保组件的渲染逻辑能够正确执行。
也就是说它们依次为前者的进一步封装。
componentUpdateFn中的初始挂载逻辑:
- 渲染组件生成
subTree;(递归调用patch) - 将
subTree通过patch挂载到container上。
这里的patch就是一个递归过程。事实上patch对于组件只有渲染过程,没有挂载的操作,因为组件是抽象的,并不能通过DOM API插入到页面上。
也就是说patch只对DOM类型元素进行mount挂载,对于组件类型元素的处理只做递归操作。换个角度描述就是:组件树的叶子节点一定都是DOM类型元素,只有这样才能渲染并挂载到页面上。
接下来开始研究patch对DOM类型元素的处理过程。(可以返回上文看一下patch的实现)。
对DOM的处理
processElement
patch函数使用processElement 函数处理新旧DOM元素,当n1为null时,走挂载流程;否则走更新流程。
源码地址:core/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts at main · vuejs/core (github.com)
const processElement = (
n1: VNode | null,
n2: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
// ...other args...
) => {
if (n1 == null) {
// 挂载
mountElement(n2, container, /* ...other args... */)
} else {
// 更新
patchElement(n1, n2, parentComponent, /* ...other args... */)
}
}
mountElement
源码位置:core/packages/runtime-core/src/renderer.ts at main · vuejs/core (github.com)
这里省略了很多代码,只保留大致流程:
-
创建DOM元素;
-
挂载子节点;
-
如果子节点只是文字,则设置DOM节点的
textContent; -
如果子节点是数组,则使用
for循环 + 递归调用patch函数渲染子元素;这里递归使用的是
patch而不是mountElement是因为子元素可能不是DOM元素,而是其它类型的元素。因此还是要用到patch中的switch - case走类型判断的逻辑。
-
-
设置
DOM元素的属性; -
插入DOM元素。
const mountElement = (
vnode: VNode,
container: RendererElement,
/* ...other args... */
) => {
const { props, shapeFlag, transition, dirs } = vnode
// 创建DOM元素
const el = vnode.el = hostCreateElement(vnode.type as string, namespace, props && props.is, props)
// 挂载子节点
if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.TEXT_CHILDREN) {
hostSetElementText(el, vnode.children as string)
} else if (shapeFlag & ShapeFlags.ARRAY_CHILDREN) {
mountChildren(vnode.children as VNodeArrayChildren, el, null, parentComponent, parentSuspense, resolveChildrenNamespace(vnode, namespace), slotScopeIds, optimized)
}
// 设置属性
if (props) {
for (const key in props) {
if (key !== 'value' && !isReservedProp(key)) {
hostPatchProp(el, key, null, props[key], namespace, parentComponent)
}
}
// 特殊处理 value 属性
if ('value' in props) {
hostPatchProp(el, 'value', null, props.value, namespace)
}
}
// 插入元素
hostInsert(el, container, anchor)
}
其中的hostCreateElement、hostSetElementText、hostPatchProp、hostInsert函数都由runtime-dom中在创建renderer的时候传入对应的实现。
在
runtime-dom模块的nodeOps.ts和patchProp.ts文件可以找到这些DOM相关操作的具体实现。
nodeOps.ts源码位置:core/packages/runtime-dom/src/nodeOps.ts at e26fd7b1d15cb3335a4c2230cc49b1008daddca1 · vuejs/core (github.com)
patchProp.ts源码位置:core/packages/runtime-dom/src/patchProp.ts at e26fd7b1d15cb3335a4c2230cc49b1008daddca1 · vuejs/core (github.com)
上述hostXXX对应的DOM方法分别是:
hostCreateElement:document.createElement;hostSetElementText:el.textContent = ...;hostPatchProp:直接修改DOM对象上的键值,会对特殊的key做处理;hostInsert:[Node.insertBefore](Node.insertBefore() - Web API | MDN (mozilla.org))
初次渲染流程总结